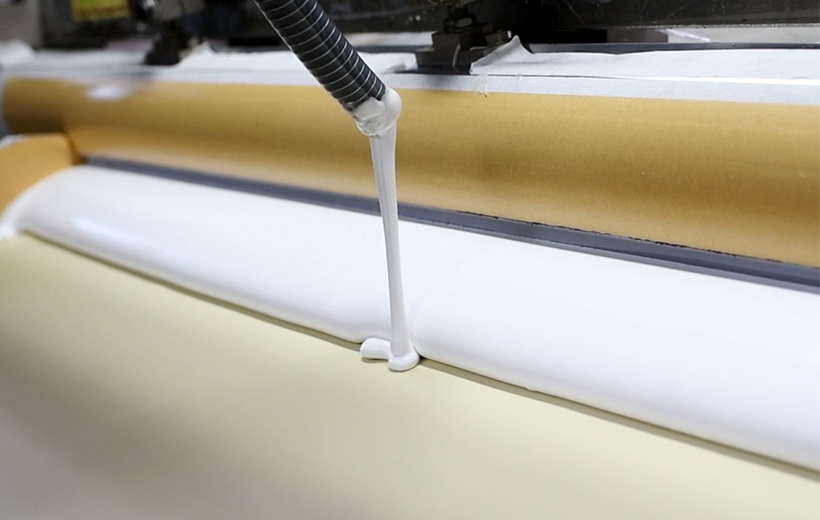
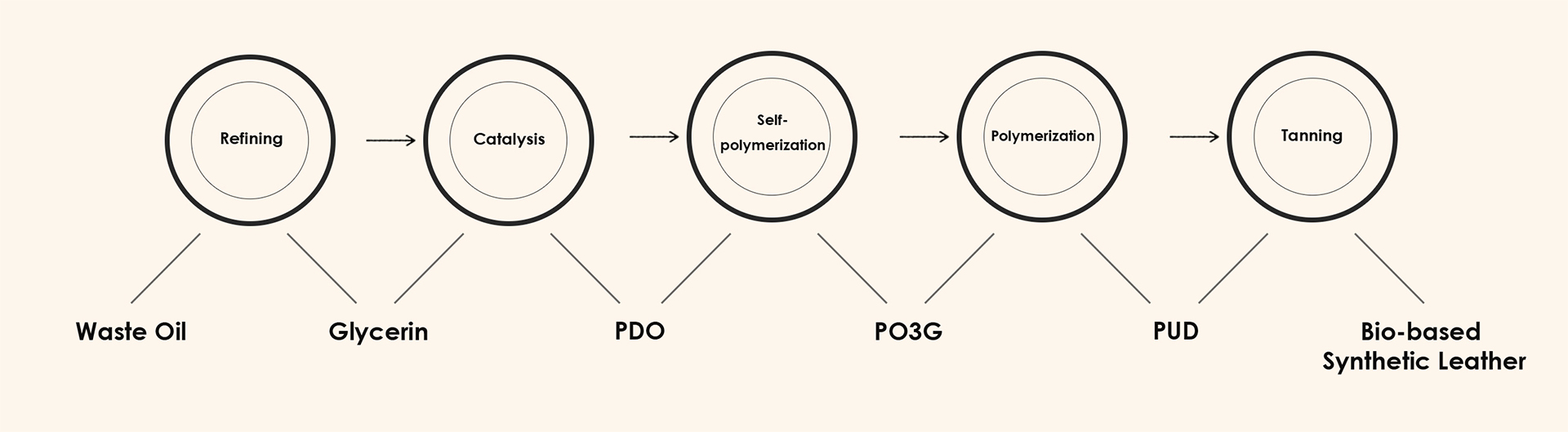
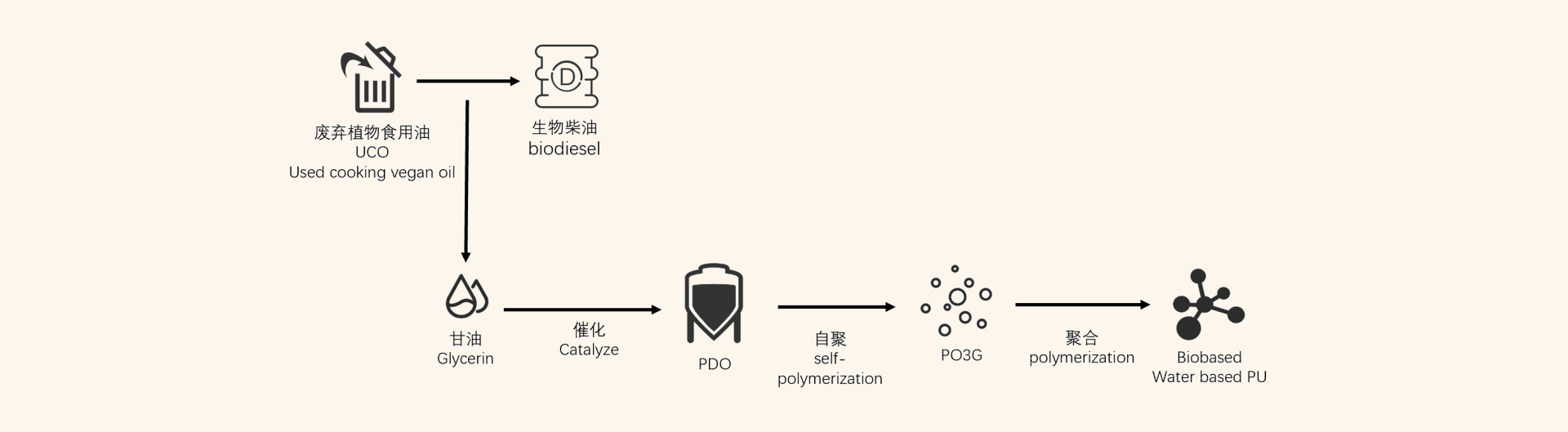
Water-based polyurethane (WPU) synthetic leather represents the eco-friendly transformation direction for industrial sustainable development. Its core advantage lies in replacing organic solvents with water-based polyurethane resins to eliminate VOCs emissions, with the key residing in the synthesis process of water-based polyurethane resins.
Mainstream Synthesis Technologies:
1. Acetone Method: Boasts strong process controllability, enabling precise construction of molecular chain structures. Solvents can be recovered and recycled, with no process wastewater generated.
2. Continuous Method: Features high automation, high efficiency, and low energy consumption. The entire process adopts a closed-loop circulation system, with no discharge of process wastewater.
Characteristics of the Production Process ChainFrom resin synthesis to leather base formation, water serves as the sole medium and cleaning carrier, recycled in a closed system. This achieves production without additional industrial wastewater, marking an innovation over traditional processes and fulfilling the commitment to green manufacturing.

The "wet base" process for traditional solvent-based synthetic leather relies on the three-phase displacement of water, dimethylformamide (DMF) and resin. It requires multiple subsequent processes, featuring a long flow, high energy consumption, and environmental pressures such as DMF recovery and emission.
Process Breakthroughs of Water-Based Synthetic Leather:
1. Replace the "wet base" line with a mechanical foaming process. After physically foaming the water-based polyurethane resin, it is dried and shaped in one go. The production line is streamlined from hundreds of meters to a single drying oven of only 40 to 60 meters.
2. Eliminate the use and residue of DMF at the source, with multiple advantages: The three-dimensional microporous structure gives the finished leather better resilience and texture, with a hand feel close to genuine leather. The thickness and stable physical properties of the foamed substrate allow for rich and long-lasting appearances without complex secondary processing, improving production efficiency and style flexibility.
The traditional solvent-based wet process was once the foundation of the synthetic leather industry. However, with high energy consumption, high pollution, and limited control over cell structure, it has become a bottleneck for sustainable development.
Core Advantages of Water-Based Mechanical Foaming Technology:
1. Environmental Protection & Carbon Reduction: Abandons toxic solvent DMF, eliminates hazardous waste and VOCs emissions. With water as the medium and efficient utilization of oven thermal energy, it complies with stringent environmental regulations.
2. Safety Assurance: Improves the working environment for production personnel. The finished products are free of toxic solvent residues, meeting the green and healthy standards for end products.
3. Excellent Performance: Precisely designs cell structure through multiple technologies, endowing the finished leather with superior physical properties such as breathability and moisture permeability. Its hand feel is close to genuine leather, making it suitable for high-end fields.
4. Advanced Technology: Transforms the complex wet chemical process into an efficient and controllable physical foaming and drying process, representing a revolutionary upgrade of the production technology.
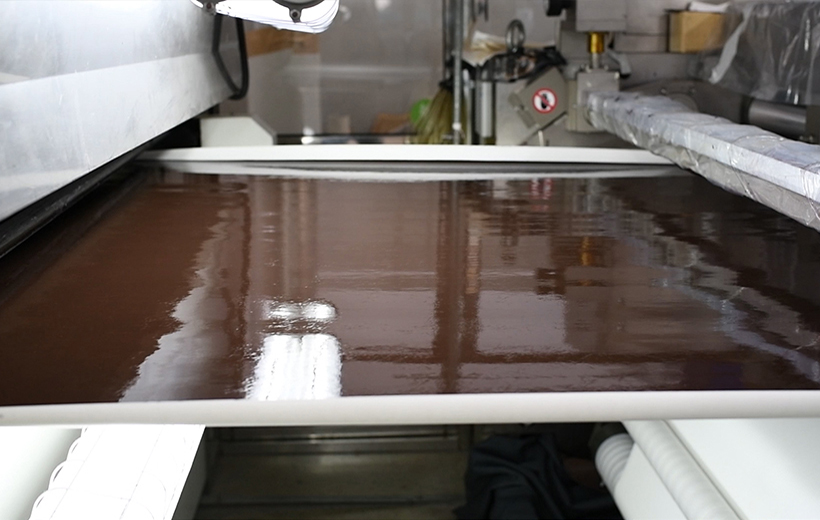

In the production of solvent-based four-way stretch synthetic leather, the traditional process naturally tolerates base fabric deformation and production line tension fluctuations, thanks to the high initial adhesion of its resin and Newtonian fluid-like properties, resulting in a relatively stable lamination process. To address the inherent low initial adhesion and pseudoplastic fluid characteristics of water-based resins, an innovative tension-free collaborative control system is introduced. Through unique mechanical and control logic, this equipment effectively offsets bidirectional tension fluctuations from both the base fabric and the production line, achieving adaptive matching and precise neutralization of tension during the critical lamination stage.
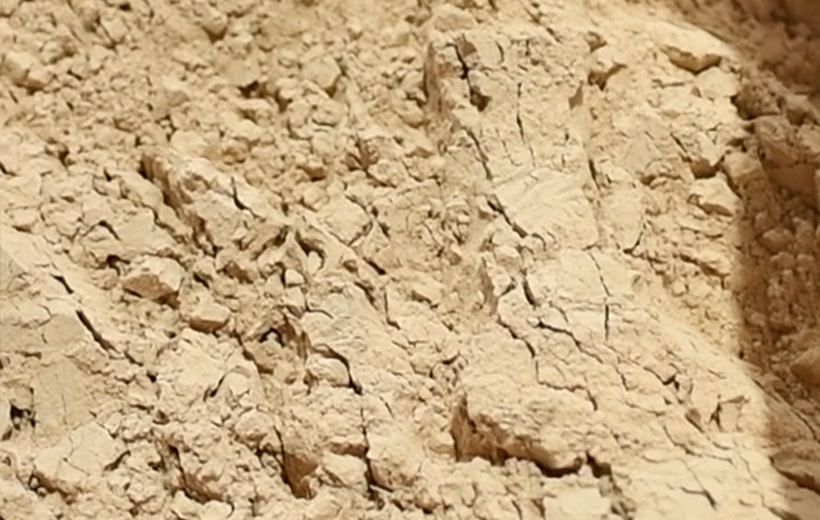

In traditional synthetic leather manufacturing, inorganic fillers such as heavy calcium carbonate and kaolin have long played a core filling role. Through innovative resource utilization technology, we convert synthetic leather scraps, biomass wastes (including coffee grounds and plant husks) into high-value functional fillers for water-based synthetic leather. By subjecting diverse raw materials from complex sources to precise drying, deoiling, and controlled grinding processes, we produce specialized powders with different particle sizes and specific surface areas. Technically, first, we develop differentiated pretreatment processes for raw materials with varying physical and chemical properties to ensure their purity and stable performance. Second, we solve the compatibility and long-term stability issues of these porous, differently polar powders in the water-based polyurethane system, enabling large-scale production. Third, through sophisticated water-based resin synthesis and additive compounding technology, we successfully construct a highly stable coating system that can accommodate and firmly bind these recycled fillers. Finally, via mature coating processes, this circular economy-oriented coating is processed into water-based synthetic leather products with excellent performance and unique texture.
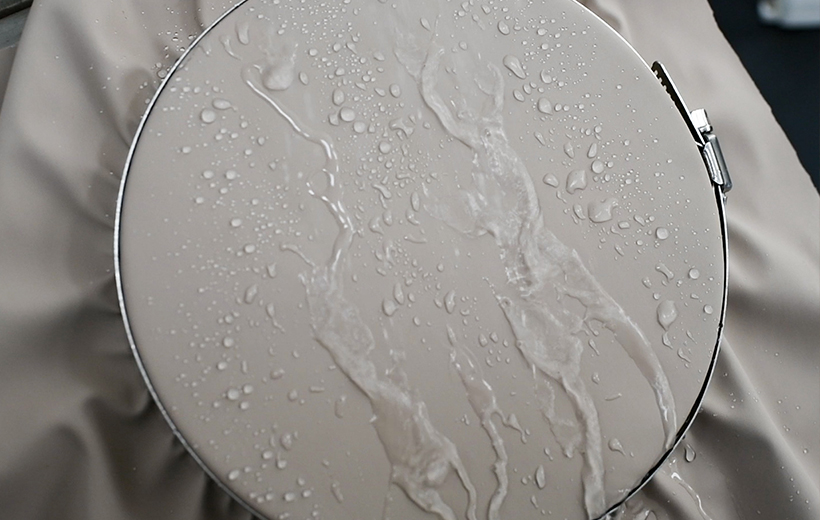

Superior waterproof performance of water-based synthetic leather is achieved through three technical dimensions:
1. Physical Structure Design: Leveraging the flexibility of molding processes, multiple bionic structures are replicated—such as micro-papillae on lotus leaf surfaces, drag-reducing ribbed structures of shark skin, or honeycomb patterns. These physically hinder water spreading and penetration, constructing the first barrier.
2. Chemical Network Crosslinking: Water-based polyurethane resins are modified to be rich in active groups like carboxyl groups. During film formation, a dense three-dimensional crosslinked network is formed, reducing pores within the film and enhancing intrinsic impermeability.
3. Special Additive Synergy: Special additives work in tandem with the chemical crosslinked network, arranging directionally on or within the coating surface. This lowers surface energy and strengthens water droplet repellency.
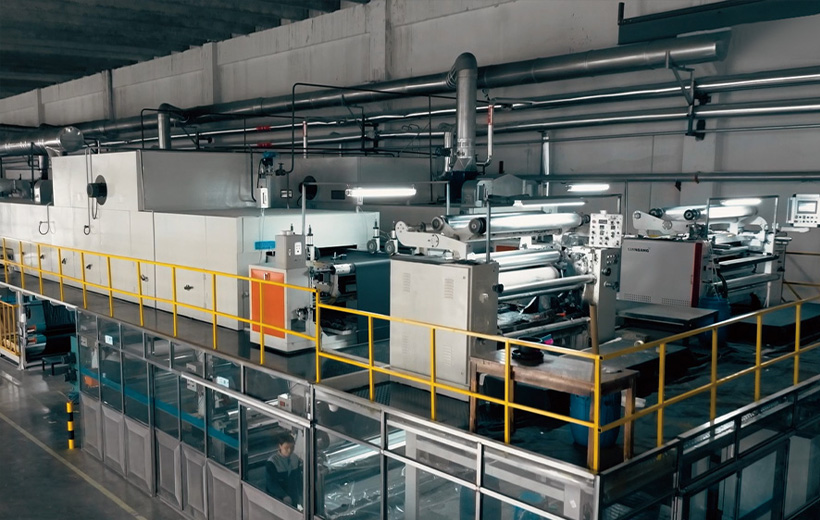

Compared with traditional wet-process synthetic leather, the water-based mechanical foaming process constructs a uniform and stable three-dimensional cell framework. The open-cell effect formed on the surface of this microstructures when in contact with release paper presets natural physical channels for moisture adsorption and transmission. The unique fluid properties and molecular design flexibility of water-based polyurethane resins enable us to precisely regulate the formed cell film walls by introducing a small amount of special functional additives, thereby interconnecting the internal closed cell structures and building efficient moisture transport channels throughout the entire foam layer.

With a micron-level coating knife system, the traditional three-layer coating is upgraded to a four-layer precision finish. It precisely controls each functional layer’s thickness and morphology, enabling water repellency, barrier property and moisture permeability.
Core Performance Implementation Paths:
1. Bionics & Surface Tension Control: Ultra-high-precision coating replicates bionic microstructures; fluorine-free water-repellent additives reduce surface energy, achieving excellent water repellency without PFAS.
2. Chemical Structure Design: The four-layer structure includes dense interface layers. Modified water-based polyurethane resins form a tight 3D crosslinked network, blocking liquid water under high hydrostatic pressure.
3. Cell & Pore Regulation: Mechanical foaming creates a uniform cell framework with micro-connected pores—smaller than water droplets but larger than water vapor molecules—ensuring superior moisture permeability and breathability.